How many gigabytes are in a terabyte? Easy guide to storage capacity.
TB, GB, MB, KB or Terabytes, Gigabytes, Megabytes, Kilobytes... they all sound similar and are often confused. Today we explain the basics of storage, the storage types, file size, and units, so that by the end of this easy guide you will know how many gigabytes are in a terabyte and vice versa.
How many gigabytes in a terabyte quick guide:


In the decimal system, there are 1000 GB in 1 TB.
There are 1024 Gigabytes (GB) in 1 Terabyte (TB) in binary and 1000 GB in 1 TB in decimal system
- 1 byte = 8 bits
- 1 kilobyte (KB) = 1,000 bytes
- 1 megabyte (MB) = 1,000 kilobytes (KB)
- 1 gigabyte (GB) = 1,000 megabytes (MB)
- 1 terabyte (TB) = 1,000 gigabytes (GB)
This table is using the decimal system.
What is a byte?
8 bits = 1 byte – the smallest unit of digital storage
First things first let’s take a look at the basics of storage to understand bytes. A byte is a unit used in computer storage and processing. A byte is made up of 8 adjacent binary digits known as bits. Each binary digit consists of a 0 or 1. Simply put, a byte is eight binary digits/bits long, and it’s the smallest unit of storage.
What is a gigabyte (GB)
When you combine bytes you get bigger units which you will have come across, for example, gigabytes, and terabytes.
A gigabyte (GB) consists of 1,000,000,000 bytes in the decimal system prefixed with Giga – which originates from the Greek word that means giant.
It’s worth noting that Gigabytes are used in different areas like science, engineering, computing, and computer science and there are two measurement systems.
- The decimal system: 1GB = 1,000,000,000 bytes
- The binary system: 1GiB (gibibyte) = 1,073,741,824 bytes (1024³)
GB is often used to explain file size, storage capacity on smartphones, on laptops, for mailboxes and for cloud storage. Understanding gigabytes and how much data they can store, can get technical – an easier solution is to look at real-life examples.
1 GB of storage and file size
- Approximately 1 HD movie
- Approximately 250 high-resolution photos
1 GB of mobile data
- Approximately 1 hour of video streaming in HD
- Browse the web for about 10 - 15 hours
- Stream music online for about 5 - 6 hours
What is a terabyte
A terabyte (TB) is a digital measuring unit with the prefix Tera. Terabytes are often used for disk drive capacity and online cloud storage solutions, for example, the basic personal plan for Dropbox offers 2 TB of cloud storage and the Tuta Mail business plan Unlimited offer 1 TB of storage.
When measuring a whole system for example the total hard drive storage capacity it’s common for it to be terabytes. This is different from individual files, images, and documents which are usually measured in GB or MB.
According to the binary system, there are 1024 gigabytes (GB) in 1 terabyte (TB), and in the decimal system there are 1000 gigabytes (GB) in 1 terabyte (TB).
To make it easier to think about data size, storage capacity, and types of storage, let’s look at real-world examples: The average high-quality image ranges from 500 KB to 2 MB. iPhones offer the lowest storage capacity of 64 GB, and according to Dropbox, 1 TB of storage is about the same as 16 64 GB iPhones.
The difference between decimal and binary memory
Decimal memory is based on the powers of 10 and is used for hard drives, USB, and SSD. Decimal memory follows the International System of Units (SI standard) and it’s what you see when you purchase a hard drive or USB stick. For example, if the hard drive says it has a memory of 1 TB it’s equal to 1 000 GB.
Binary memory on the other hand is based on powers of two and is used for operating systems for example Linux, macOS, and Windows. According to the Joint Electron Engineering Council (JEDEC) in the binary system, 1 TB is equal to 1024 GB.
Below we’ve put together a table to see the difference between decimal and binary according to the SI and JEDEC standard.
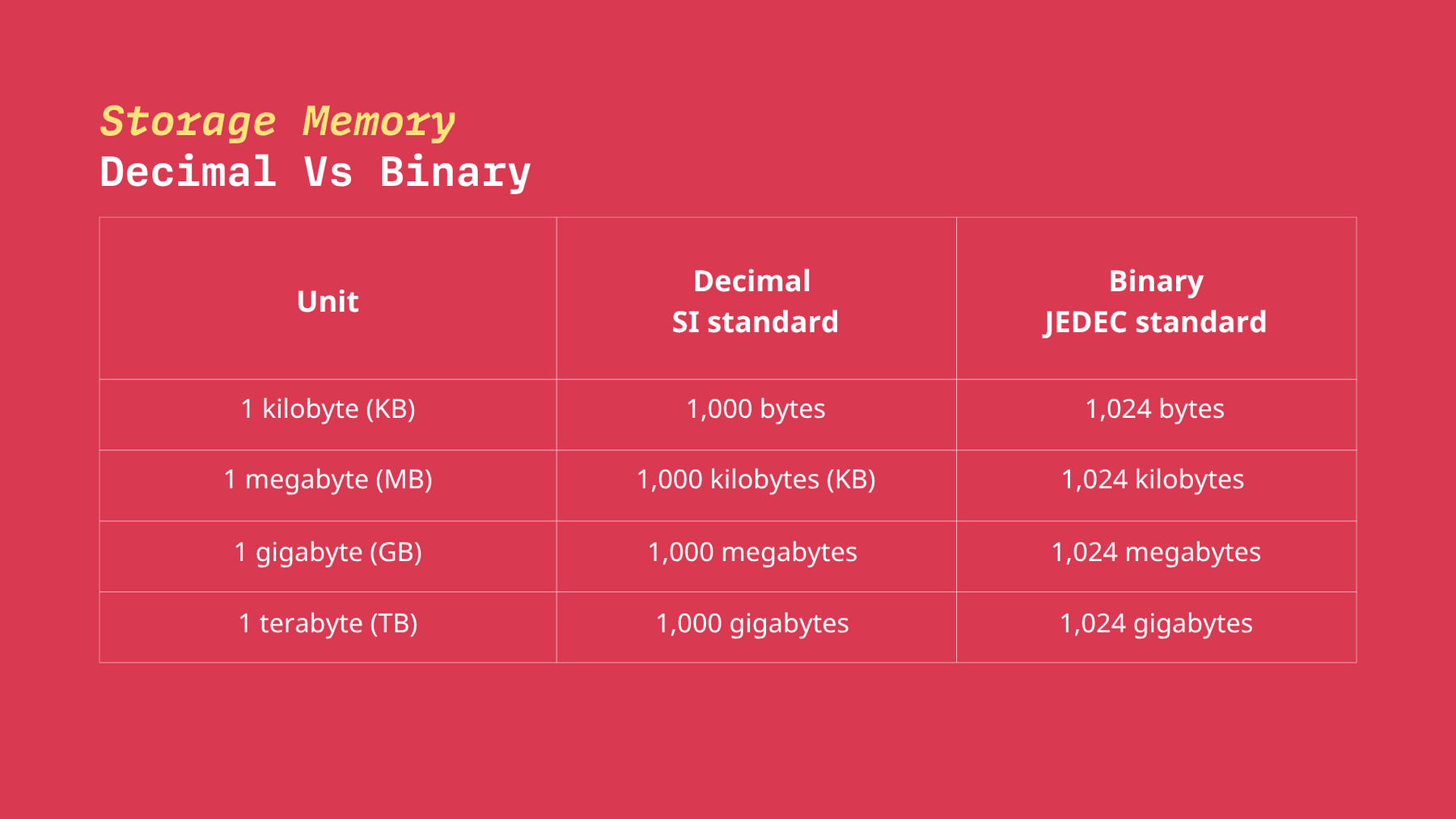

Decimal memory is based on the powers of 10 whereas binary memory is based on the powers of two. Each memory type is used in different industries. For example, hard drives use decimal memory and operating systems use binary memory.
Email Storage
Tuta Mail is a German-based email provider that offers users around the world a simple and easy way to send end-to-end encrypted emails to anyone. Tuta Mail offers both free and paid plans that all come with ample email storage space allowing you to store confidential emails privately. Let’s take a look at how much storage the personal plans and the business plans of Tuta Mail come with.
It’s also worthy to note that Tuta compresses all data stored on its servers so that in fact you get more storage than what it actually says, making Tuta Mail not only the best in terms of security, but also in terms of storage capacity.
Tuta Mail storage for personal use:
- Free: 1 GB
- Revolutionary €3 /month: 20 GB
- Legend €8 /month: 500 GB
Tuta Mail storage for business use:
- Essential €6 /user/month: 50 GB/user
- Advanced €8 /user/month: 500 GB/user
- Unlimited €12 /user/month: 1000 GB = 1 Terabyte/user
Storage FAQ
- How many megabytes in a gigabyte
According to the decimal system, there are 1,000 megabytes in a gigabyte. If using the binary system, there are 1,024 megabytes in one gigabyte.
- How many kilobytes in a gigabyte
In the decimal system, there are 1,000,000 kilobytes in 1 gigabyte. If using the binary system, there are 1,048,576 kilobytes in 1 gigabyte.
- Is 1TB 1000 or 1024 GB?
In the decimal system, 1 TB is 1,000 GB. If you’re using the binary system, 1 TB is 1,024 GB.