Encrypted emails, calendars & contacts
Tuta is the go-to service to securely store your data in the cloud. Its built-in encryption makes sure that your data stays secure, no matter what. Your encryption key belongs to you, and to you alone. It is never shared with anyone else, not even with Tuta.
Tuta is the world's most secure email service because we protect your data at all ends. Whether on our servers, or on your devices: In Tuta all data is always end-to-end encrypted.
Encrypted mailbox
The entire mailbox – emails, calendar and address book – are stored end-to-end encrypted in Tuta. The only unencrypted data are mail addresses of users as well as senders and recipients of emails. Upon entering your login credentials, your mailbox is automatically decrypted locally on your device.
Data that Tuta encrypts end-to-end:
- Emails, including subject lines and all attachments
- Entire calendars, even metadata such as event notifications
- Entire address book, not just parts of the contacts
- Inbox rules / filters
- And the entire search index.
Tuta automatically encrypts all emails between Tuta users end-to-end, which makes a great difference to online security as a whole. Tuta even lets you send end-to-end encrypted emails to anyone regardless of the email provider that they use.
Encrypted emails to anyone
Tuta uses symmetric (AES 256) and asymmetric encryption (RSA 2048 or ECC (x25519) and Kyber-1024 as quantum-safe algorithms) to encrypt emails end-to-end. When both parties use Tuta, all emails are automatically end-to-end encrypted (asymmetric encryption). For an encrypted email to an external recipient, a password for encrypting & decrypting the email (symmetric encryption) must be exchanged once. You can then use the same password for any conversation with that specific contact: With Tuta you don’t need to set a new password for each email sent to the same contact.
Tuta’s automatic encryption works easily on all mobile and desktop devices. The encryption key is never shared with anyone else, including Tuta. Therefore, even if a malicious attacker intercepts the email message, they will not be able to read its content or attachments.
Encrypted calendar
Tuta is the first end-to-end encrypted calendar ever developed. The Tuta calendar encrypts all data, even the attendees of an event are stored encrypted.
The Tuta calendar is the only zero-knowledge calendar out there because even when you get a push notification for an upcoming event, we have built this reminder service in such a way that our servers never see the notification. This will keep our servers in the dark not just about what events you are having, but also when your events are taking place.
Any calendar that sends notifications via email can’t be considered zero-knowledge, even if the email notifications are encrypted because sending the notification itself already involves the server which leaks information. That's why we have gone to great lengths to push encrypted notifications directly to the Tuta clients, for instance to our desktop and mobile apps, and handle these notifications locally on your own device – not on our servers. The big plus with the mobile apps is that you also receive these reminders when you are not actively using the app.
Check our post about our first release of the calendar to learn why encrypted notifications are so important to protect your privacy.
Innovative encryption
How Tuta's encryption process works
Tuta's innovative encryption method secures your private key so that you - and only you - can access your data from any device.
Tuta uses an innovative encryption method to secure your data easily. Tuta is the only email service that automatically encrypts all emails, all calendars and all contacts by default. Key generation, key handling, key exchange – all of this happens automatically in the background, yet, the private key is still only accessible by the user.
When a user registers a secure Tuta email account, the browser, Tuta app, or desktop client automatically generates a private and a public key locally on their device. The private key is encrypted with the help of the user’s password before it is transmitted to Tuta’s servers in highly secured data centers in Germany.
While many seemingly secure cloud services store private keys openly on a central server, this has never been an option for us.
Your password becomes the private key
In Tuta, the private key is encrypted with the user’s password so that only the user can access it. No one else, not even we as the developers of Tuta, can access the private keys stored encrypted on our servers.
Read here why a private key must not be stored on a central server unencrypted.
How is the password secured in Tuta?
As the user's password is central to the security of the encrypted data stored in the Tuta mailbox, we have to make sure that the password is secured at all times. Tuta never sends the password to the server in plain text in order to authenticate the user.
To secure the login password, Tuta uses Argon2 and SHA256. Thus, the login password is only used indirectly to authenticate the user with the server and to encrypt / decrypt the private key.
This is shown by the following picture and explained in the text below:
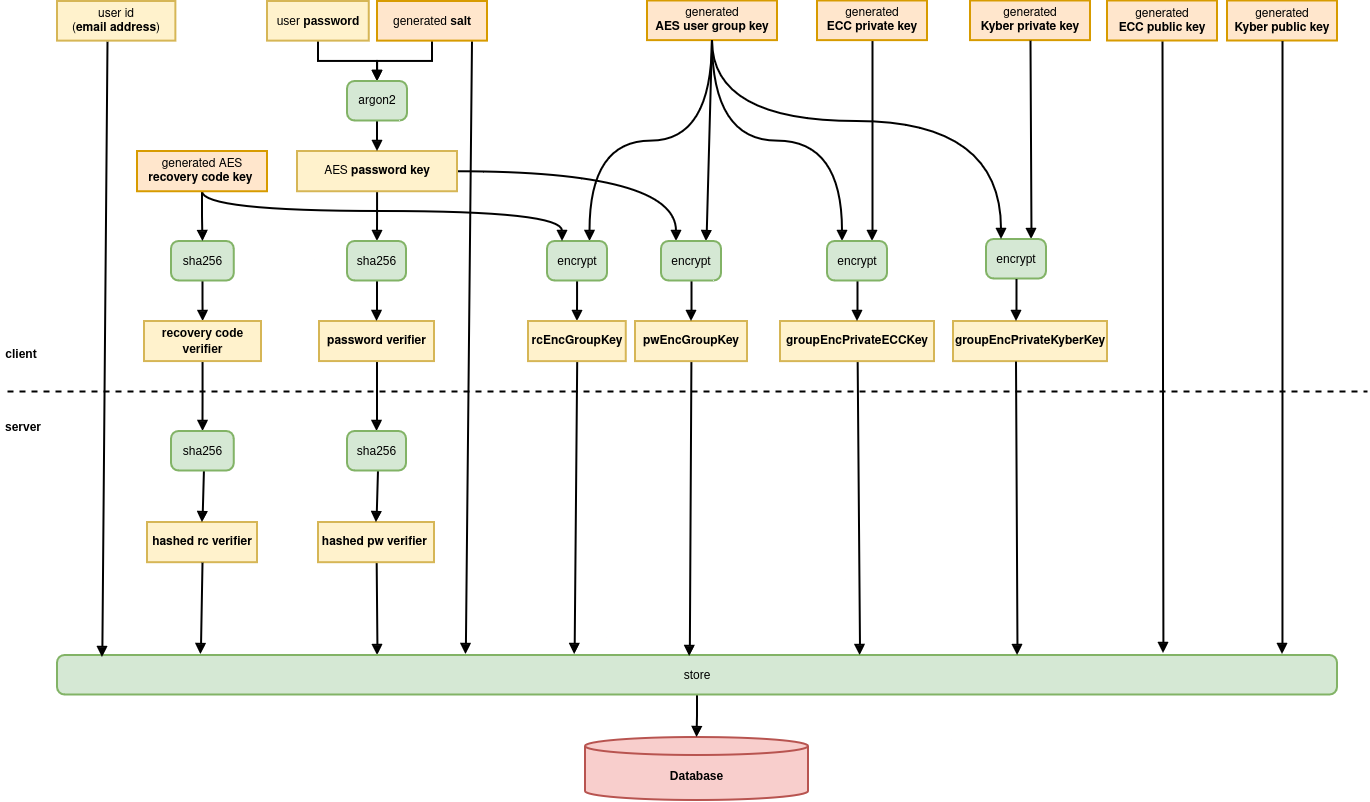
Argon2 modifies the password so that it becomes the “AES password key”. This AES password key is used to encrypt the private RSA-key (though via an indirection with the private symmetric “AES user group key”).
The AES password key itself, however, is not used to authenticate the user with the server, but it is hashed to become the “password verifier”.
This password verifier is then transmitted to the server to authenticate the user. The server itself only stores the password verifier as another hash ("hashed verifier") so that it is impossible to use the persistent data on the server to login.
The password verifier is cryptographically independent from the password key so that the password verifier can not be used to decrypt any data. The password verifier is transmitted to the Tuta server secured with TLS encryption.
Should a third person gain access to the password verifier via a TLS vulnerability, he would not be able to gain access to the private key or to the end-to-end encrypted data stored in the encrypted Tuta mailbox.
The decryption process takes place locally on the device of the user once the user has been authenticated with the server.
By encrypting the private key with the user’s password, Tuta can automatize the entire encryption process without ever having access to your private key.
Why does Tuta Mail not use PGP?
Tuta uses standard algorithms also being used by PGP (AES and RSA or ECC) for encrypting the entire mailbox. In addition, Tuta Mail already uses post-quantum cryptography (Kyber) for quantum safe accounts, which is still a work in progress for PGP. Furthermore, Tuta does not use an implementation of PGP itself because PGP lacks important requirements that we have for Tuta:
PGP does not encrypt the subject line (already achieved in Tuta),
PGP algorithms can't be easily updated, e.g. to post-quantum secure ones like in Tuta Mail,
PGP has no option for Perfect Forward Secrecy (already achieved for Tuta in a prototype).
In Tuta we can easily update the algorithms, and we plan to replace the current algorithms with quantum secure hybrid protocol in the near future. The flexibility of Tuta enables us to integrate an encrypted calendar, encrypted cloud storage and many more features much easier and faster than it would have been possible with an implementation of PGP.
Why Tuta Mail does not offer S/Mime support
Another email encryption protocol used by businesses as email solutions is S/Mime.
For S/MIME a certificate needs to be installed on the email clients of the recipient and the sender. When an email is sent, the sender encrypts the email using the recipient's public key and the recipient decrypts the email using the private key.
However, in May 2018, the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) announced critical vulnerabilities in S/MIME, together with an obsolete form of OpenPGP that is still used in many email clients. Dubbed EFAIL, the bug required significant coordinated effort by many email client vendors to fix this vulnerability. However, to date, it is not clear whether all email services actually did fix the issue.
Post-quantum secure encryption
Tuta is not only the most secure email service at the moment, we will also stay the most secure one in the future.
That's why we are the first email provider to have worked out a protocol for post-quantum secure encryption. We are introducing this protocol, initially for new and ultimately for all Tuta accounts, started in March 2024. This lets us encrypt emails with a hybrid approach combining our proven encryption algorithms with post quantum secure algorithms.
We stay ahead of the game by updating to post-quantum cryptography and make sure that your data stays secure, even when quantum computers will be able to break currently used encryption algorithms.
Encrypt Everything
Whenever you communicate with Tuta - receive a notification about a new email, execute a search, enter a calendar entry, add a new contact to your address book - your data is always sent end-to-end encrypted. We never send unencrypted data via notifications, and we never allow unencrypted data to be stored on your device.
You can check for yourself what data Tuta encrypts!
What data does Tuta encrypt?
Tuta encrypts as much data as possible directly on your device. You can verify this yourself: When logged in in a web browser, press F12 to open the developer console. Then click on 'Network' and 'Preview' to see what data is sent to the server. This view is updated every time you open an email, a contact or a calendar entry. All texts that are rendered in non-readable form by humans are sent to the server end-to-end encrypted and Base64-encoded.
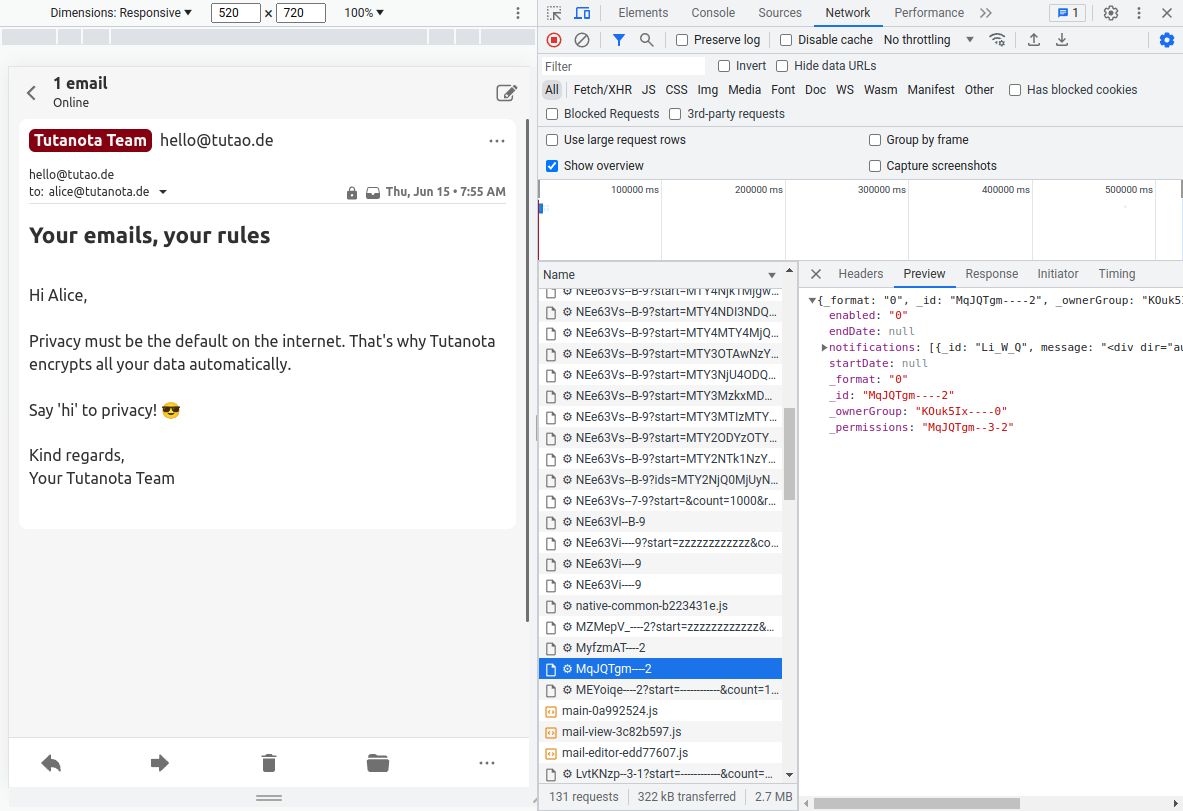
The screenshot shows the encrypted email contents. Similar to PGP, Tuta encrypts the data of an email end-to-end with a hybrid encryption protocol based on symmetric and asymmetric cryptography.
Your signature is appended to new mails automatically. With Tuta, your signature is stored end-to-end encrypted on our server and synchronized on all of your devices.
As Tuta does not use PGP, it can encrypt a lot more data of an email than just the contents. This is illustrated by the next screenshot.
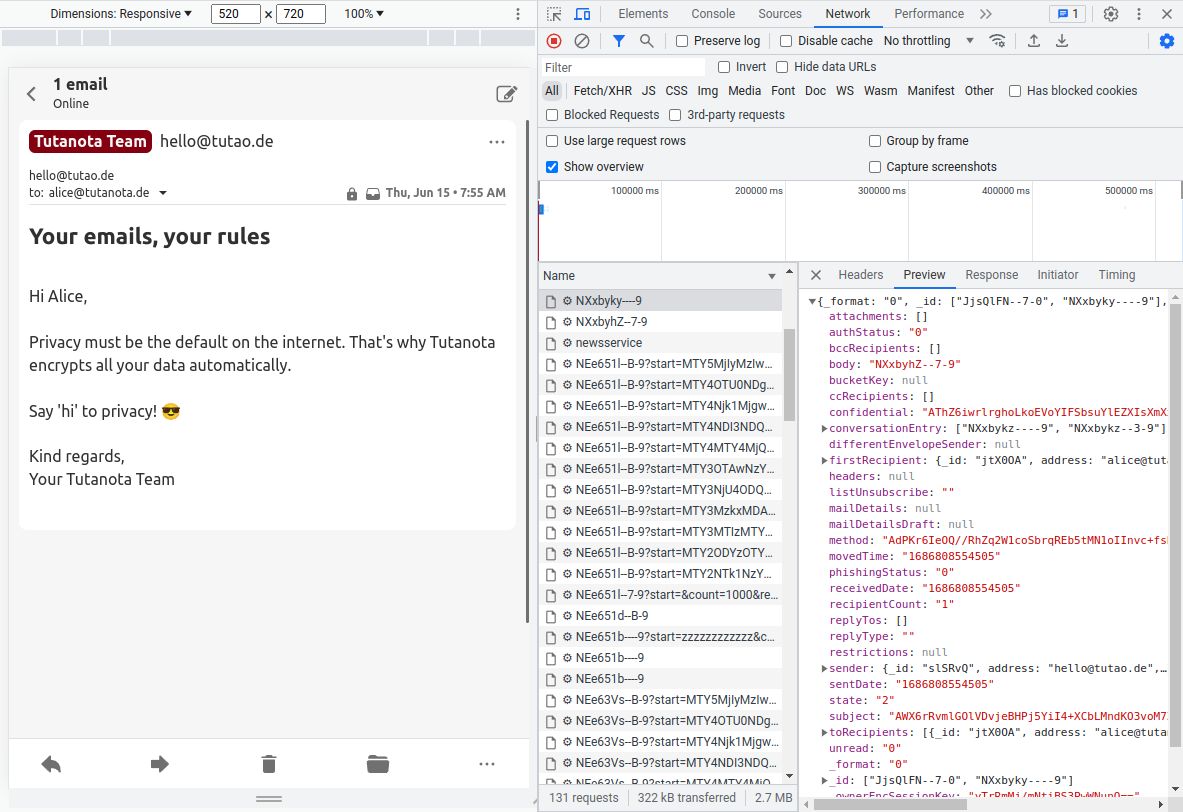
As you can see, Tuta encrypts the "subject" as well as the names of the "sender" and the recipient ("toRecipients").
The only data that is not encrypted in a Tuta email are the email addresses and the date of an email sent or received. Due to the way the email protocol is set up, it is not possible to encrypt this information as other email servers need to see where the email should be delivered to.
Regarding email security, there are two different cases:
End-to-end encrypted emails sent between Tuta users or to users of other mail systems.
Mails that are sent or received in unencrypted form to/from users of other mail systems.
In both cases, all emails are stored fully encrypted on our servers. We never store unencrypted emails on our servers. However, the non-encrypted emails are not protected with end-to-end encryption, but are only encrypted once they reach our servers.
Calendar
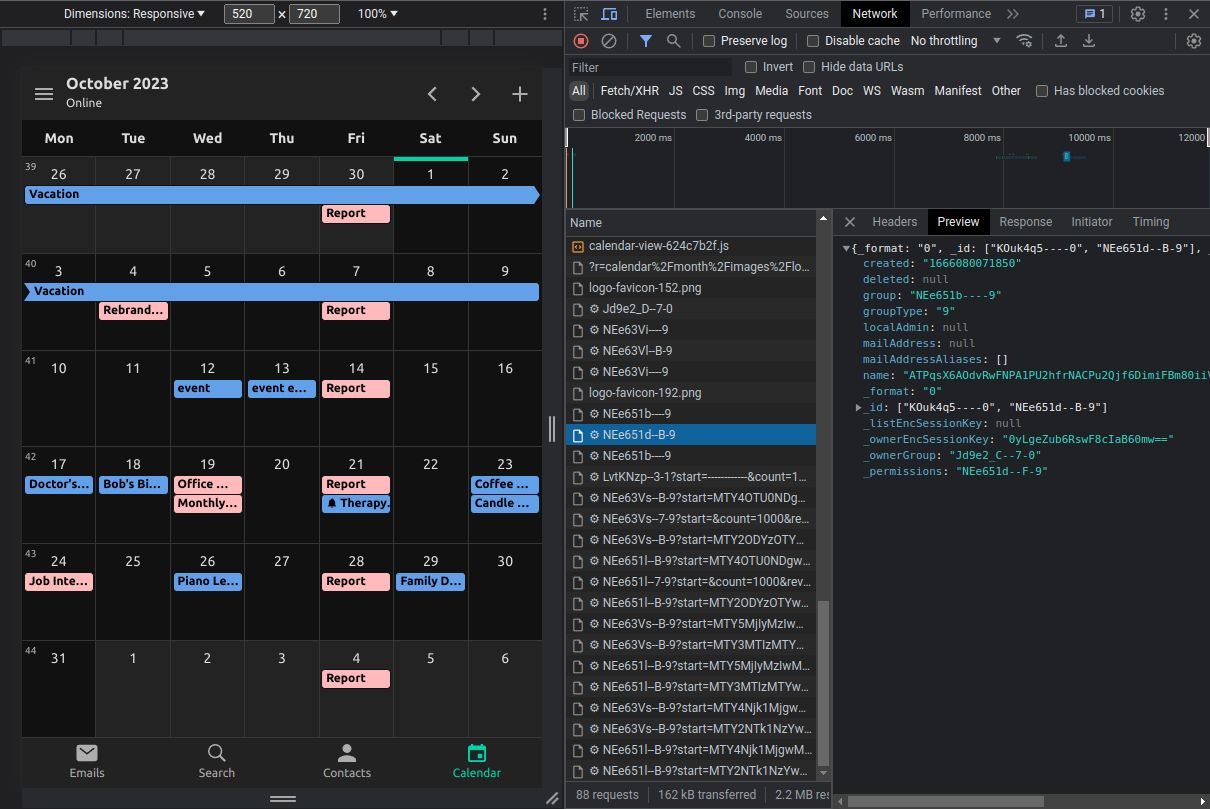
The Tuta Calendar is the only true zero-knowledge calendar because our servers know nothing about your encrypted events. All data that you store in the calendar is encrypted: The "description", the "endTime", the "location", the "startTime", the "summary", the "uid" (the ID of the event), the "alarmInfos" (which are the reminders that you can define to be notified about upcoming events), and the "repeatRule" (which is the rule to define in what interval and until what date the event should be repeated).
The Tuta Calendar also encrypts notifications, which is a very innovative approach. The encrypted Tuta alarms are stored locally on your devices to completely hide them from our servers. This means we do not know anything about your calendar events, not even when an event is taking place.
In contrast to that, current standards such as iCal do not encrypt any data. If you store your events with an online service for easy access and syncing, you can be sure that someone else is seeing all your calendar events.
In the zero-knowledge Tuta Calendar all your data is always encrypted so that no one, not even we as the developers, can see your private appointments.
Contacts
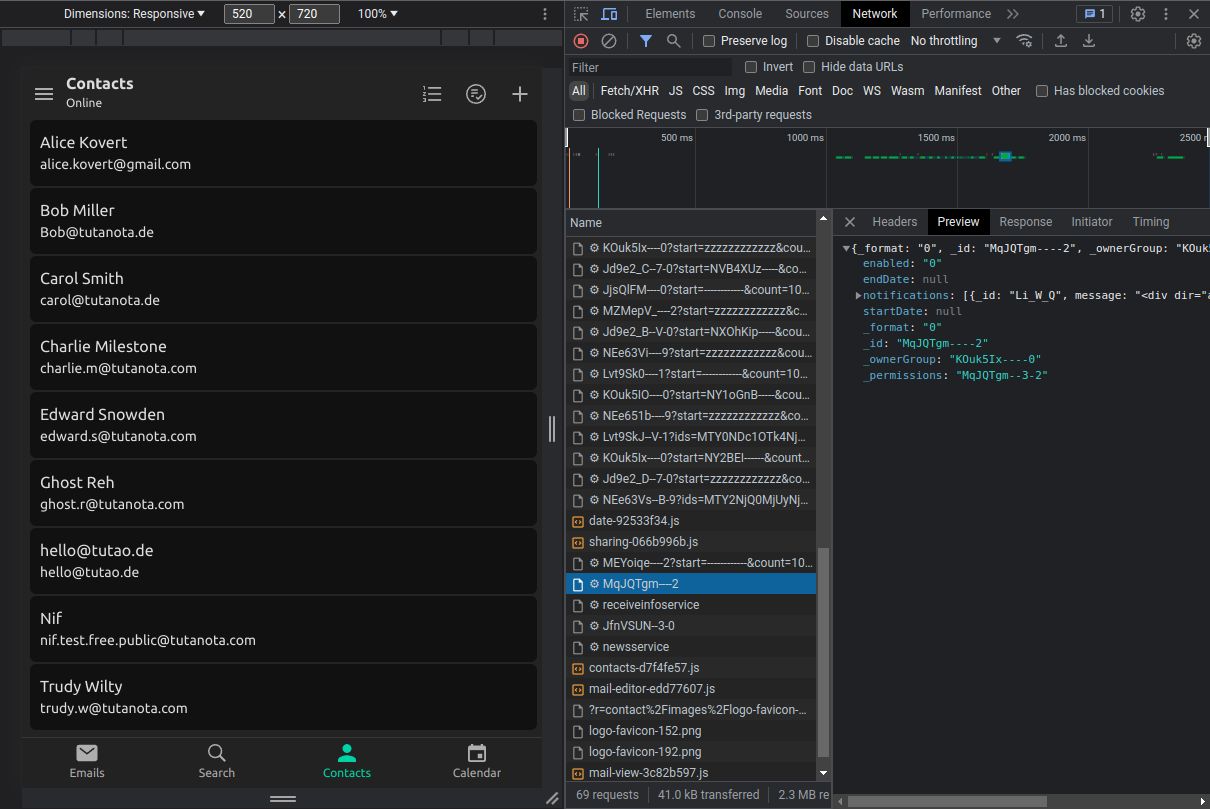
Tuta Contacts are encrypted entirely, just like the Tuta Calendar. You can store all your contacts details in Tuta knowing that no one but yourself can get access to this very personal information of your family members, your friends or your business contacts.
Tuta automatically encrypts the "birthdayISO", the "comment", the "company", the "firstName", the "lastName", the "nickname", the "role", the "title", the "addresses", the "mailAddresses", the "phoneNumbers", and the "socialIDs".
Expect more
Tuta offers more than just easy email encryption. Tuta makes sure that all your data is always encrypted and can only be accessed by one single person: You.
Tuta automatically encrypts all your emails, calendars and contacts.
Tuta brings automatic encryption to all your devices. Whether you're at home, at work or on the go, encrypting all your data has never been easier.
Switch to Secure Emails Today
Fast, sustainable, open source, simple migration process. Email to feel good about.